In the urinary system, the bladder plays the role of a collector storage collector: exhausted blood filter products come from the kidneys through the urethra.Thanks to the bladder and two muscle rings, one of which obeys conscious commands of the central nervous system, a healthy person can perform urination as needed, need and opportunities.The "opportunity" in the early stages of evolution was intended, first of all, a secure atmosphere;With the advent and development of human civilization, urination began to seek special conditions, ie, a division into social activity, a specially created place and/or solitude by representatives of the opposite sex.
Cystitis is an inflammatory process on the inner walls of the bladder;A disease that causes pronounced physiological and psychological discomfort as well as a certain social malice.A person of any age and gender may face this disaster, but it is no coincidence that cystitis is sometimes called a modern woman's curse (it would be more accurate to say "one of the curses", as this is not the only disease).The main reason lies in anatomy: compared to the male female urethra (urethra) is much shorter, more elastic, wider and fairer.This creates an extremely suitable "gate" for the penetration of urogenital infections into the climb, the spread and variety of which in the modern world is really great.And, although not every cystitis has an infectious nature, is the described mechanism of its development which is a major factor in inter-shower epidemiological changes: according to various sources, in active age women, cystitis occurs 6-8 times more often than in men.
In general, statistical analysis allows you to evaluate the problem at different angles.So many sources show that at least a single life -lifetime attack is experiencing at least half of all women;At a minimum, every fourth is periodically or chronically ill (some authors even consider these data very low, as not all sick people seek a doctor).According to medical documentation, in the clinics, among all urological patients, the portion of patients with cystitis reaches 67%;In urological hospitals, this indicator is 5-12% (in other words, the hospitalization percentage is also very high, which confirms once again the social importance of this disease).The frequencies of acute and chronic forms are approximately 2: 1.
The difference in the incidence between the floors is flattened with the elderly and the elderly age: in older age categories, the percentage of men initially with cystitis is comparable to a similar percentage of women.But at a mature, young, young (and sometimes in teens or even children) age, when you live, it will seem, to rejoice!- Cystitis is waiting and mainly chooses women.
Reason
From infections, the bladder wall is protected by nature, in principle, quite well;The predominance of infectious etiology of the cystitis is not due to sensitivity as such, but by a combination of a high probability of infection with adverse external and internal conditions, most of which are somewhat lifelong.The main risk factors include any acute and chronic infection in other body systems (from caries and colitis to acute viral respiratory infections -sexually transmitted diseases), hypothermia, hypovitaminosis, after surgical impoverishment, unhealthy, excessive and permanent diet of sleep, permanent "Healthy, good preference, which is synthesized, which is synthesized, which is synthesized.Hormonal background fluctuations (in particular, cystitis irritations associated with the menstrual cycle phase, pregnancy or menopause are considered separately in the literature).
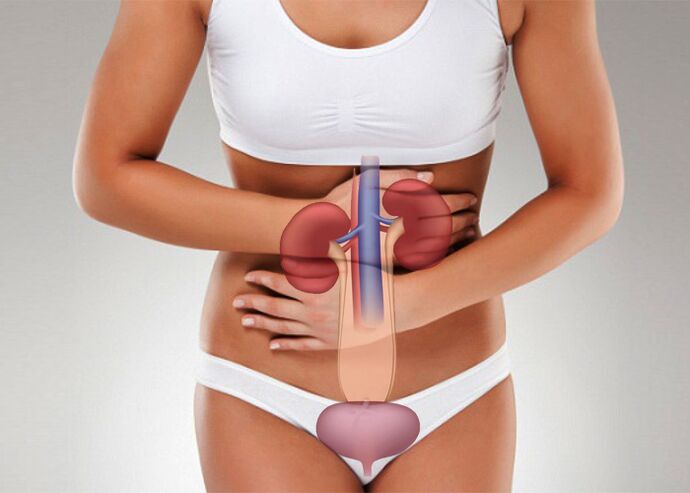
We also note that the infection can penetrate the bladder not only as it climbs, but also the descending trails - from the kidneys affected by the nephritis.
Non-infectious forms include chemical-toxic (including medicines), allergic, radiation, traumatic, parasitic.
Symptoms
Classic cystitis symptoms include, first of all, intensive discomfort during urination: rub, pain, burning, etc.Often, urination leaves the feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;Many patients complain of repeated or false stimulation, notice the "flow" of urine to freedom or the necessary nature of stimulation (because, again, anatomical reasons are more natural in women who often "do not have time to run" and therefore are forced to stay closer to the toilet).In some cases, clouding or a mixture of blood in the urine is detected;Hematuria should be said to be the most dangerous urological symptom and requires immediate differential diagnosis, as the presence of blood in the urine can be caused not only by cystitis but also for the causes of life.
Typical and, as a rule, severely expressed with the cystitis of pain syndrome: attraction or spicy, bursting or pain in the lower abdomen, often with radiation in the claws or spine.Without such pain or the like, no more than 10% of the entire cystitis persists.With a sufficient immune response, general mistreatment, fever, weakness, headaches are often intense.
The most likely and severe cystitis complications include SO -Called its interstitial shape, when not only the mucosa, but also a deeper layer of bubble wall muscles is involved in the inflammatory process (after all it can lead to bubble wrinkles and its pronounced failure), as well as the spread of infection, the spread of the infection, the infection,Many, many, making a consequence of questioning.infertility, etc.).
Troubleshooting

In addition to a clinical study and a standard urological inspection (however, many women prefer to treat cystitis not with a urologist, but for their "gynecologist"), laboratory tests are mainly described.So far, many of all types of methods for detecting the pathogen are successfully used - as shown above, the most likely cause should always be considered a bacterial, viral or fungus infection.As a diagnostic, ultrasound, less than cystoscopy, less than cystography, biopsy and other studies are prescribed.
Troubleshooting
In addition to a clinical study and a standard urological inspection (however, many women prefer to treat cystitis not with a urologist, but for their "gynecologist"), laboratory tests are mainly described.So far, many of all types of methods for detecting the pathogen are successfully used - as shown above, the most likely cause should always be considered a bacterial, viral or fungus infection.As a diagnostic necessity, an internal bladder study is also described, an X -Ray study of the bladder, biopsy and other studies.
Treatment
Acute cystitis in chronic curves often, easily and insidious: the gradual decrease in symptoms, even its complete disappearance, means no cure.Therefore, the cystitis signs described above in any of their combinations (especially since these symptoms are natural in many other urological diseases) require an immediate visit to the doctor, and not the patient's expectations while "passes".Along the way, we note that a large number of good, smart, friendly, proven for centuries and other similar online tips (where you can find recommendations in the rank from quite reasonable to schizophrenic or fraudulent) is one of the frequent chronic factors and cystitis complications.
Based on the results of the diagnostic examination, a particular, always strictly individual regimen of treatment is always described, intended, first of all, to eliminate the cause of inflammation.In various cases, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, antifungal, immunomodulators and immunostimulants, antihistamines and anti -inflammatory drugs can be used.Chronic focuses of infection in other areas, as well as the treatment of background diseases (nephrolithiasis, prostate adenoma, etc.) are required.Moreover, a diet is required, increased fluid consumption and saving of the regime to avoid hypothermia and other risk factors.Phytotherapeutic agents are exclusively prescribed by a doctor, and he also controls the effectiveness of their administration.
Depending on these conditions, the cystitis cures.




























